Research
Recent research themes
Shape Measurement of Nano-shape using a Scanning Laser Interferometer with Wide Field of View
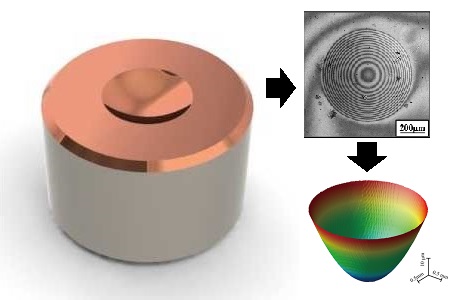
Aspheric lens mold requires high shape accuracy. However, there are few non-contact methods that can measure the entire surface of large mold in a short time. Laser microscope developed in our laboratory has wide field of view, however the resolution in the depth direction is low. Therefore, we installed a reference plate and have developed a method to calculate the mold’s three-dimensional form by treating the interference fringes as contour using the principle of interference.
Nanoscale Measurement of Whole Cylindrical Surface using a Wide Field of View Laser Interferometer
Cylindrical surface can be observed with a laser microscope with wide field of view by scanning the laser along the bus direction and rotating the cylinders. Generally, there is a trade-off relationship between the field of view and resolution in the depth direction. The resolution in the depth direction of laser microscope with wide field of view became low. In this study, we have supplemented the low resolution in depth direction by introducing a reference plate. Ultimately, the resolution in the depth direction improve to nanometer level.
Detection Method of Nano-level Defects by using Microscope with Wide Field of View
With the miniaturization of design rules in LSI, micro or nano scale scratches will affect the device property. Thus, inspection techniques of scratches of such size have became important. A laser microscope with wide field of view developed in our laboratory can be applied to observe surface to be inspected with high resolution and wide field of view, and may be suitable as a device for micro scratches inspection. In this study, we observed scratches of various size from nano to micro by using the laser microscope with wide field of view. We examined how the tiny nano-scratches appeared thought the laser microscope.
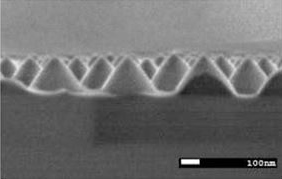
Improvement of Pedicle Screw Fixation
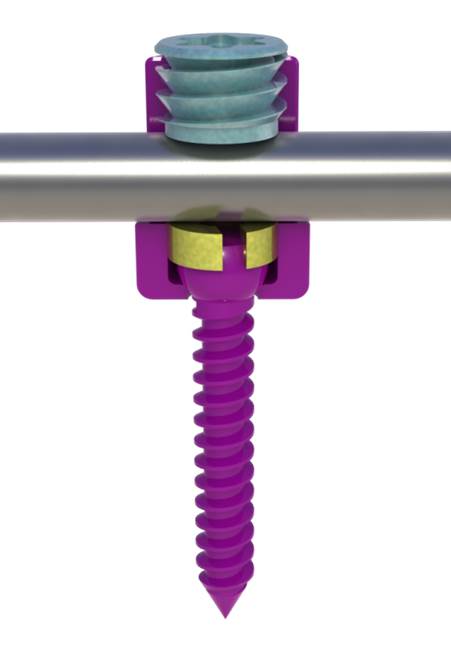
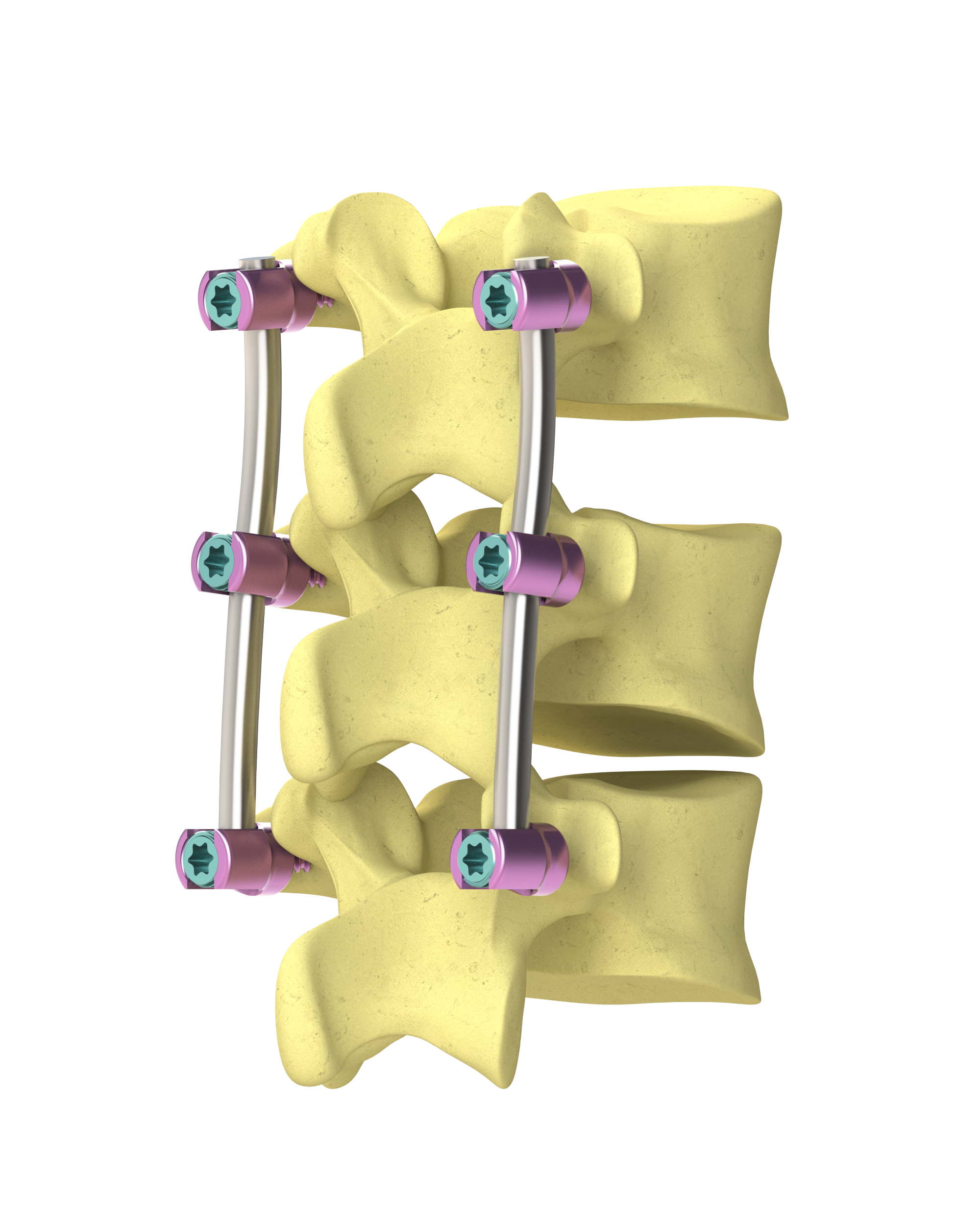

Pedicle screw fixation is a surgical treatment for idiopathic scoliosis patients especially of serious cases. Size reduction of this implant is required for better QOL of the patients. It is important for size reduction to develop high friction surface without any constraints for medical use. We developed the high friction surface by laser micro-texturing on practical implant surface. In this study, we have observation and analysis on the friction surface, the effect of laser micro texturing on the frictional properties were clarified.
Research of Artificial Bones by Selective Laser Sintering with Laser Fine Processing Machine
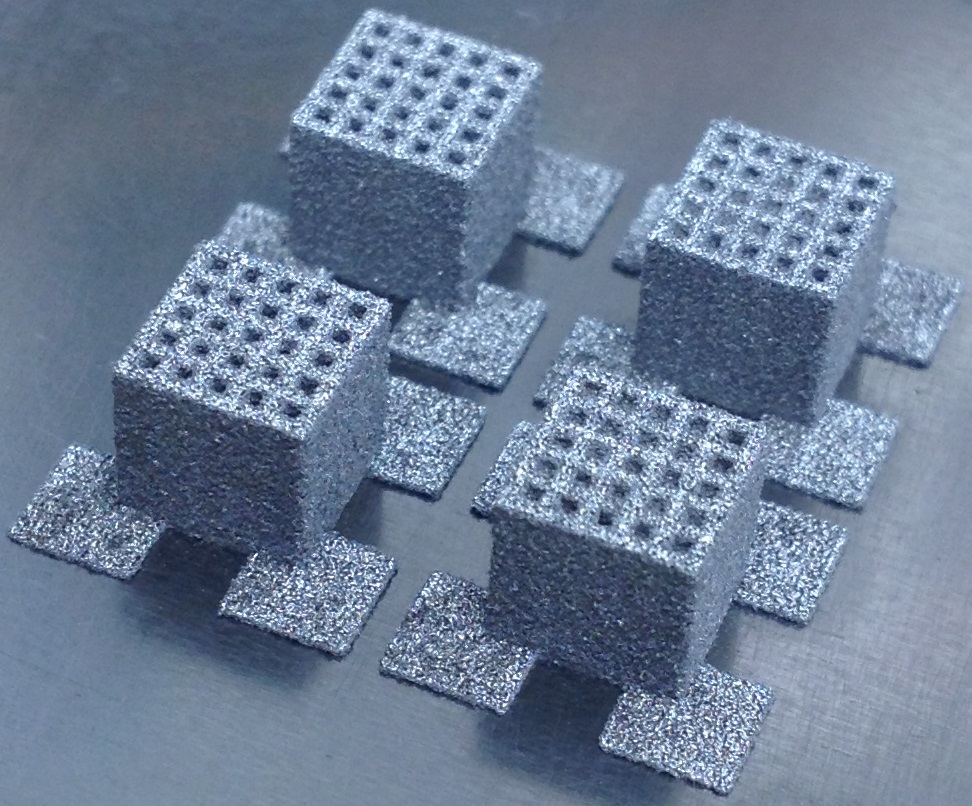
There is an increase in demand of artificial bones because the number of the osteoporosis patients increased in step with the aging of population.
The artificial bone is an implant that compensate missing bone caused by injury or and sickness.
In general, the artificial bone is made of biomaterial such as hydroxy apataite.
But it is low in strength to support load.
Therefore, a material with high biocompatibility and strength is required.
The titanium artificial bones have high biocompatibility and high strength.
But the Young’s modulus is more than 100GPa that is about 10 times of original bone.
The difference in Young’s modulus causes some problems like slip and concentrated load.
To solve this problem, we carried out selective laser sintering to manufacture titanium artificial bone.
The structure made by laser sintering had much airspace, and the mechanical property resembled real bones with low Young’s modulus.
And, an annealing in vacuum prompted surface diffusion that made stronger bonding between sintering powders.
Therefore we study artificial bones that have structure with airspace and high load bearing.
Clarification of Deformation behavior of Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Film
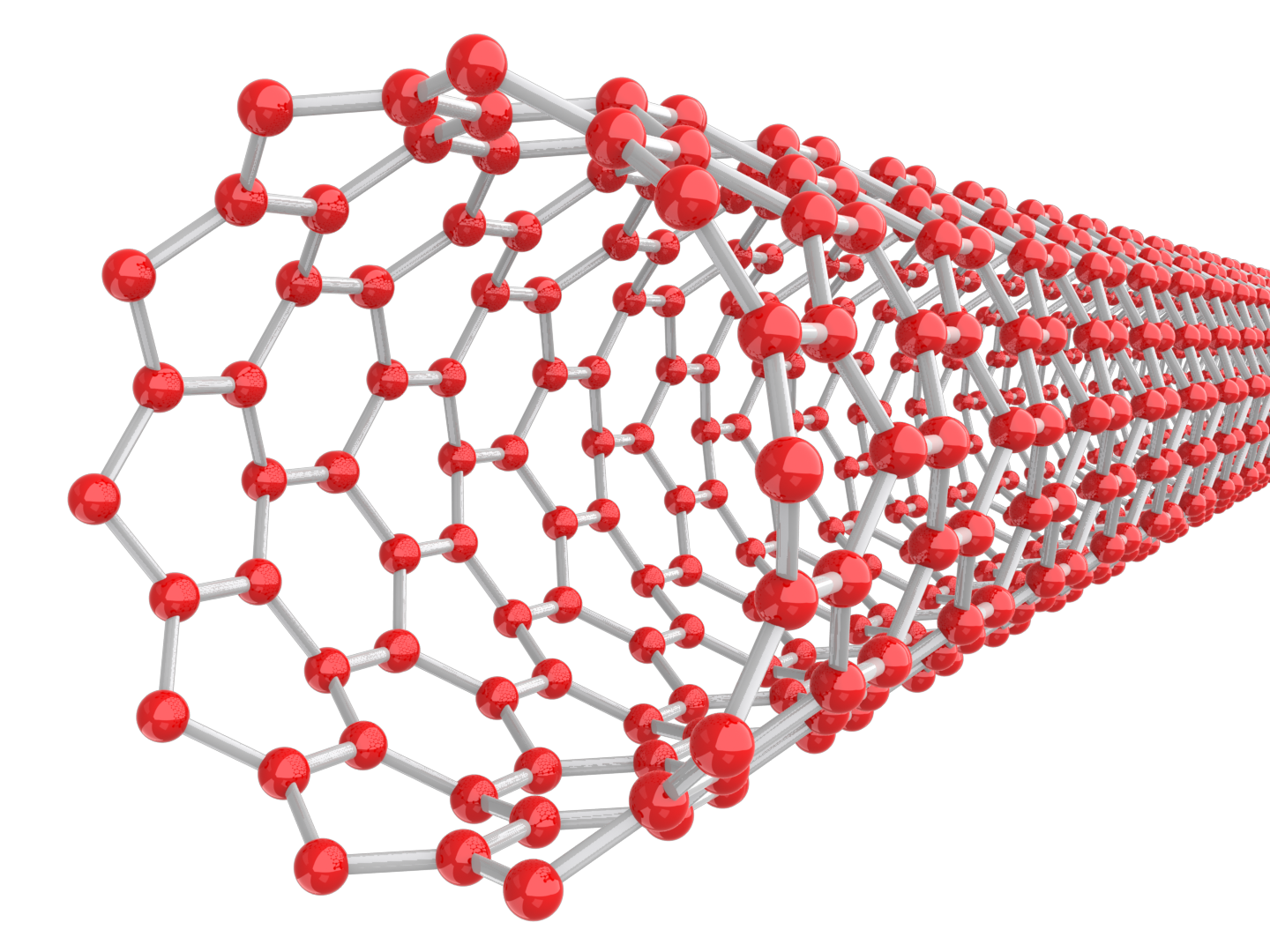
CNT is an elongated tube of nanoscale and has excellent flexibility and thermal conductivity. The CNT film which is produced by the SiC surface decomposition method is referred to as Vertically Aligned CNT film. Vertically aligned CNT film is expected as a superior low contact thermal resistance material, but the microscopic deformation behavior of CNT in contact is not clear. The vertically aligned CNT film was brought into contact with a plano-convex lens, and the contact surfaces were observed using a laser microscope with both high resolution and wide field of view. We clarified the difference in the deformation behavior by analyzing states of the contact surfaces.
Measurement of Contact Thermal Resistance of Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Film
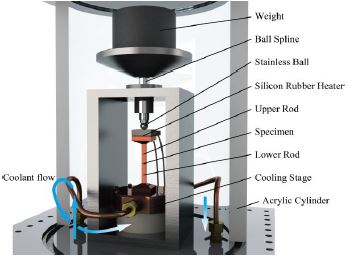
Carbon nanotubes have been reported to have high thermalconductivity. A vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VA-CNT) film is composed of densely packed and highly-aligned CNTs on a SiC substrate. This VA-CNT film is expected to have superior heat conductivity than a conventional thermal-grease heat transfer method. However, it is not clear that how much contact pressure and contact roughness affect the contact thermal conductivity of the VA-CNT films. We developed anapparatus that measures the contact thermal resistance by anone-directional steady-state heat flow method. We found out that therewas suitable surface roughness for the minimum contact thermalresistance of the VA-CNT film.
Contact Behavior and Frictional Properties of Rubber Roller for Printer

As for the quality of printing, tribological factors associated with rubber roller are important. The width of contact is wide for commerical microscopes. (A4-size : 260mm, A3-size : 330mm) Thus, we used laser microscope with wide field microscope by installing low nummerical aperture objective lens. Consequently, The slip distance and the real contact area of each contact points were obtained.
Study of Laser Coordinate Measuring Machine

There is a problem when body structure is assembled in manufacturing of railway trains. a body structure is vehicle body of railway trains. when it is assembled, it will be anchored by welding to the body structure of each panel. however, railway trains itself are changed because heat by sweating each panel ingenerate a strain. in the past, there is no how to measure quantitatively this strain, deformation amount of railway trains, so it takes a long time at revised work. this study represents the amount of change in the quantitative measurement using laser coordinate measuring machine, that aims to reduce the processing time to fix.